|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1. Security Services (Overview) Part II System, File, and Device Security 2. Managing Machine Security (Overview) 3. Controlling Access to Systems (Tasks) 4. Virus Scanning Service (Tasks) 5. Controlling Access to Devices (Tasks) 6. Using the Basic Audit Reporting Tool (Tasks) 7. Controlling Access to Files (Tasks) Part III Roles, Rights Profiles, and Privileges 8. Using Roles and Privileges (Overview) 9. Using Role-Based Access Control (Tasks) 10. Role-Based Access Control (Reference) Part IV Solaris Cryptographic Services 13. Solaris Cryptographic Framework (Overview) 14. Solaris Cryptographic Framework (Tasks) 15. Solaris Key Management Framework Part V Authentication Services and Secure Communication 16. Using Authentication Services (Tasks) 19. Using Solaris Secure Shell (Tasks) 20. Solaris Secure Shell (Reference) 21. Introduction to the Kerberos Service 22. Planning for the Kerberos Service 23. Configuring the Kerberos Service (Tasks) 24. Kerberos Error Messages and Troubleshooting 25. Administering Kerberos Principals and Policies (Tasks) Ways to Administer Kerberos Principals and Policies Administering Kerberos Principals 26. Using Kerberos Applications (Tasks) 27. The Kerberos Service (Reference) 28. Solaris Auditing (Overview) 29. Planning for Solaris Auditing 30. Managing Solaris Auditing (Tasks) |
Administering Kerberos PoliciesThis section provides step-by-step instructions used to administer policies with the SEAM Tool. This section also provides examples of command-line equivalents, when available. Administering Kerberos Policies (Task Map)
How to View the List of Kerberos PoliciesAn example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
Example 25-9 Viewing the List of Kerberos Policies (Command Line)In the following example, the list_policies command of kadmin is used to list all the policies that match *user*. Wildcards can be used with the list_policies command. kadmin: list_policies *user* testuser enguser kadmin: quit How to View a Kerberos Policy's AttributesAn example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
Example 25-10 Viewing a Kerberos Policy's AttributesThe following example shows the Policy Details panel when you are viewing the test policy. 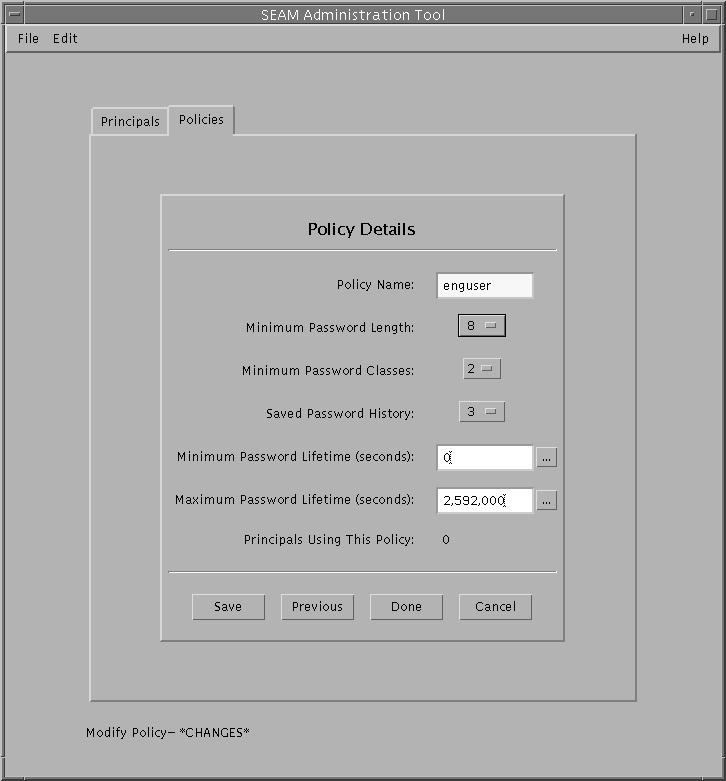 Example 25-11 Viewing a Kerberos Policy's Attributes (Command Line)In the following example, the get_policy command of kadmin is used to view the attributes of the enguser policy. kadmin: get_policy enguser Policy: enguser Maximum password life: 2592000 Minimum password life: 0 Minimum password length: 8 Minimum number of password character classes: 2 Number of old keys kept: 3 Reference count: 0 kadmin: quit The Reference count is the number of principals that use this policy. How to Create a New Kerberos PolicyAn example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
Example 25-12 Creating a New Kerberos PolicyIn the following example, a new policy called build11 is created. The Minimum Password Classes is set to 3. 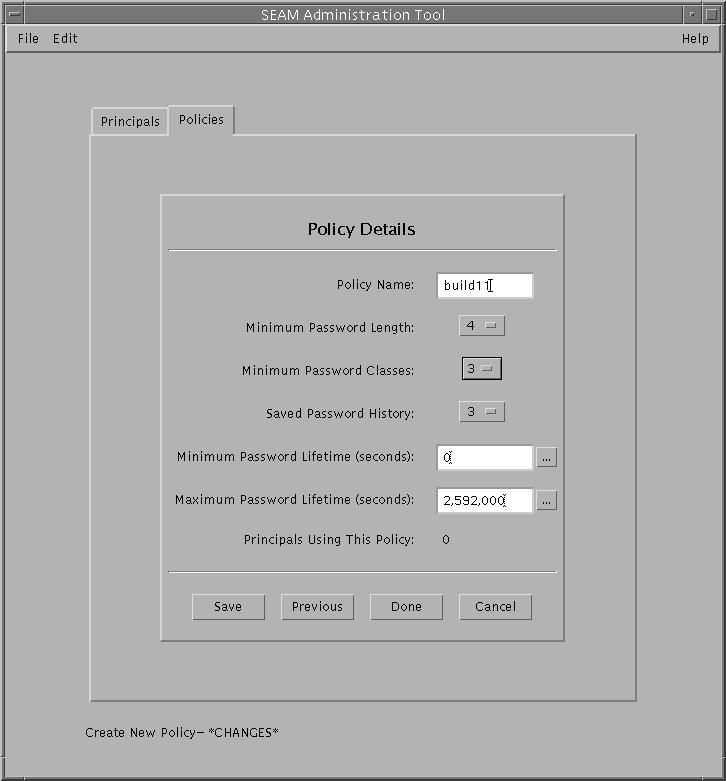 Example 25-13 Creating a New Kerberos Policy (Command Line)In the following example, the add_policy command of kadmin is used to create the build11 policy. This policy requires at least 3 character classes in a password. $ kadmin kadmin: add_policy -minclasses 3 build11 kadmin: quit How to Duplicate a Kerberos PolicyThis procedure explains how to use all or some of the attributes of an existing policy to create a new policy. No command-line equivalent exists for this procedure.
How to Modify a Kerberos PolicyAn example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure.
Example 25-14 Modifying a Kerberos Policy (Command Line)In the following example, the modify_policy command of kadmin is used to modify the minimum length of a password to five characters for the build11 policy. $ kadmin kadmin: modify_policy -minlength 5 build11 kadmin: quit How to Delete a Kerberos PolicyAn example of the command-line equivalent follows this procedure. Note - Before you delete a policy, you must cancel the policy from all principals that are currently using it. To do so, you need to modify the principals' Policy attribute. The policy cannot be deleted if any principal is using it.
Example 25-15 Deleting a Kerberos Policy (Command Line)In the following example, the delete_policy command of the kadmin command is used to delete the build11 policy. kadmin: delete_policy build11 Are you sure you want to delete the policy "build11"? (yes/no): yes kadmin: quit Before you delete a policy, you must cancel the policy from all principals that are currently using it. To do so, you need to use the modify_principal -policy command of kadmin on the affected principals. The delete_policy command fails if the policy is in use by a principal. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|